Reliability and fallback
How WorkflowAI is designed to provide 100% uptime for your agents.
Goal
We are committed to delivering 100% uptime for the API endpoints that power your agents, including:
https://run.workflowai.com/v1/chat/completions(compatible with OpenAI SDKs)https://run.workflowai.com/v1/[org-id]/tasks/[agent-id]/schemas/[schema-id]/run(for WorkflowAI SDKs)
Current system status
WorkflowAI API
Operationalrun.workflowai.com
98.9% uptime
TODO: add status monitor showing uptime metrics and tokens processed per day
Intelligent fallback systems
WorkflowAI implements multiple layers of fallback mechanisms to ensure your agents continue running even when individual components fail. These systems work together to provide seamless operation across different failure scenarios.
Provider fallback (automatic)
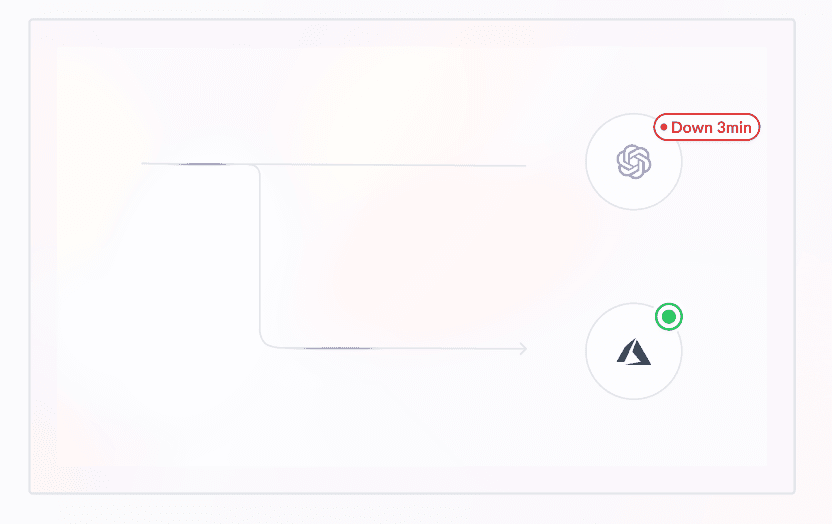
WorkflowAI continuously monitors the health and performance of all integrated AI providers. When a provider experiences downtime or degraded performance, our system automatically switches to a healthy alternative provider without any manual intervention.
For example, all OpenAI models are also available through Azure OpenAI Service. If the OpenAI API becomes unavailable, WorkflowAI will automatically failover to Azure OpenAI within one second. This seamless transition ensures your agent runs continue without interruption, and you don't need to make any changes to your code.
This intelligent routing between providers happens behind the scenes, maintaining consistent response times and reliability for your applications even during provider outages.
Model fallback (configurable)
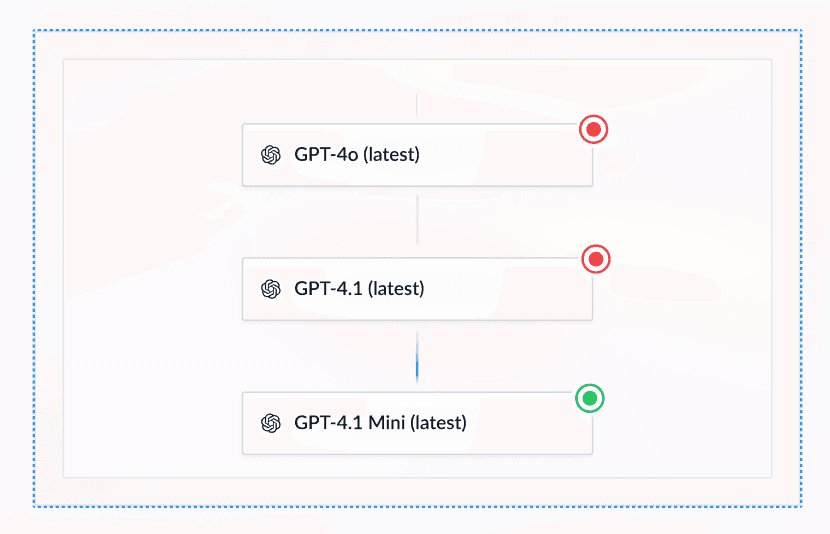
Sometimes using the exact same model on a different provider won't ensure 100% uptime. Common scenarios include:
- The model doesn't have provider redundancy and the unique provider is having issues
- All providers for a given model are down, or rate limits are exceeded on all providers
- The completion failed due to model limitations (content moderation errors, failed structured outputs)
In these cases, falling back to a different AI model can ensure the completion succeeds.
Configuration options
Configure model fallback using the use_fallback argument in the completion endpoint:
| Option | Value | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Automatic (default) | "auto" | Uses a different model based on the error type. See automatic fallback logic below. |
| Disable | "never" | Disables fallback entirely. Useful when consistency matters more than success. |
| Custom | ["model-1", "model-2"] | Allows passing a list of models to try in order when the initial model fails. |
Configuring model fallback is only available through code for now.
Automatic fallback logic
The default fallback algorithm (i.e. when use_fallback is not provided or when use_fallback="auto") assigns each model a fallback model based on the type of error that occurred:
- for rate limit errors, we use a model of the same category (similar price and speed) that is supported by a different provider
- structured generation errors can occur for models without native structured output. In this case, we use a model at the same price point that supports native structured output. For example,
GPT 4.1 Nanowould be used as a fallback for models likeLlama 4 ScoutandGemini 2.0 Flash. - for content moderation errors, we use a model that has been historically more permissive. For example, Llama 4 Maveric on Groq seems to be on the stricter side whereas non preview Gemini models on Vertex are often more permissive.
The exhaustive fallback definitions are visible in the codebase
Code examples
OpenAI SDK
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Extract the name and email"}],
extra_body={
"model_fallback": ["gpt-4o-mini", "claude-3-5-haiku-20241022"]
},
metadata={"agent_id": "user-extraction"}
)const completion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o",
messages: [{"role": "user", "content": "Extract the name and email"}],
// @ts-ignore
model_fallback: ["gpt-4o-mini", "claude-3-5-haiku-20241022"],
metadata: {"agent_id": "user-extraction"}
});curl -X POST https://run.workflowai.com/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $WORKFLOWAI_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-4o",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Extract the name and email"}],
"model_fallback": ["gpt-4o-mini", "claude-3-5-haiku-20241022"],
"metadata": {"agent_id": "user-extraction"}
}'WorkflowAI SDK
@workflowai.agent(id="user-extraction", version="production", use_fallback=["gemini-2.0-flash-001", "o3-mini-latest-medium"])
def user_extraction(_: UserExtractionInput) -> UserExtractionOutput:
...const extractUser= workflowAI.agent<UserExtractionInput, UserExtractionOutput>({
id: 'user-extraction',
schemaId: 1,
version: 'production',
useFallback: ['gemini-2.0-flash-001', 'o3-mini-latest-medium'],
});curl -X POST https://run.workflowai.com/v1/agents/user-extraction/schemas/1/run \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $WORKFLOWAI_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"version": "production",
"use_fallback": ["gemini-2.0-flash-001", "o3-mini-latest-medium"],
"task_input": ...
}'Infrastructure resilience
Our infrastructure is designed with multiple layers of redundancy to ensure continuous operation even during various failure scenarios.
Application layer
We've designed our application architecture for maximum resilience:
- Isolated inference endpoints: Our inference API
run.workflowai.comruns in separate containers, isolated from other API endpoints. This allows independent scaling and deployment of the inference API. - Canary deployments: New API versions are deployed to a small subset of users first, then gradually rolled out. This allows us to catch issues early and roll back if needed.
- Health monitoring: Continuous monitoring of service health enables automatic failover and issue detection.
Database layer
We use MongoDB Atlas for our primary database infrastructure, ensuring high availability through a distributed architecture with a 99.995% SLA. Our database deployment includes 7 replicas across 3 Azure regions:
- 3 replicas in East US2
- 2 replicas in Iowa
- 2 replicas in California
These replicas automatically synchronize data, ensuring that if one database instance or even an entire region fails, others can immediately take over without data loss. MongoDB Atlas offers automatic failover capabilities, where if the primary node becomes unavailable, a secondary replica is automatically promoted to primary, typically within seconds.
For storing run history and analytics data, we use Clickhouse, which excels at handling large volumes of data efficiently. While Clickhouse powers our analytics and observability features, it's not required for core agent execution. The process that stores run history is completely isolated from the critical run path, ensuring agents continue running normally even if Clickhouse experiences temporary unavailability.
Network & datacenter layer
We use Azure Front Door as our global load balancer to ensure high availability across multiple regions. Our infrastructure is deployed in both East US and Central US datacenters, providing geographic redundancy.
Azure Front Door continuously monitors the health of our backend services in each region. If one datacenter experiences an outage or performance degradation, Azure Front Door automatically redirects traffic to the healthy region within approximately 30 seconds. This intelligent routing happens without manual intervention, ensuring minimal disruption to your API calls.
This multi-region architecture allows us to maintain high availability even during regional cloud provider outages, helping us achieve our goal of 100% uptime for the WorkflowAI API.
If you have any questions about our architecture, please contact us.
How is this guide?